Hrc Fuse Rating Chart: Understanding the Essentials
In the realm of electrical safety and circuit protection, the term “HRC Fuse” often comes into play. But what exactly is an HRC fuse, and how do you determine the right rating for your specific application? In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of HRC fuse rating charts, demystify their significance, and equip you with the knowledge needed to ensure electrical safety in your projects.
Introduction
Electrical circuits are the lifeblood of modern technology, but they come with inherent risks. To mitigate these risks and protect electrical systems from overcurrents, short circuits, and other faults, various safety devices are used. One such device is the High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) fuse. In this article, we will explore HRC fuses in detail, with a specific focus on understanding the HRC fuse rating chart.
What is an HRC Fuse?
HRC stands for High Rupturing Capacity, which is a crucial property of fuses. An HRC fuse is a type of electrical safety device designed to interrupt the flow of current in a circuit when excessive current levels are detected. These fuses are engineered to withstand and safely interrupt fault currents, preventing potential electrical disasters.
Why is the Fuse Rating Important?
The fuse rating is a critical parameter when it comes to HRC fuses. It determines the current-carrying capacity of the fuse and plays a pivotal role in protecting electrical equipment and preventing overheating. Choosing the right fuse rating is essential to ensure the safety and reliability of your electrical system.
Components of an HRC Fuse
Before diving into the intricacies of fuse ratings, let’s take a moment to understand the components that make up an HRC fuse. Typically, an HRC fuse comprises the following elements:
- Fuse Element: This is the heart of the fuse, responsible for carrying and interrupting the current flow.
- Fuse Body: The outer casing that houses the fuse element.
- End Caps: These secure the fuse element within the fuse body.
- Contacts: The terminals that connect the fuse to the circuit.
- Indicator: Some HRC fuses feature indicators that show whether the fuse has blown.
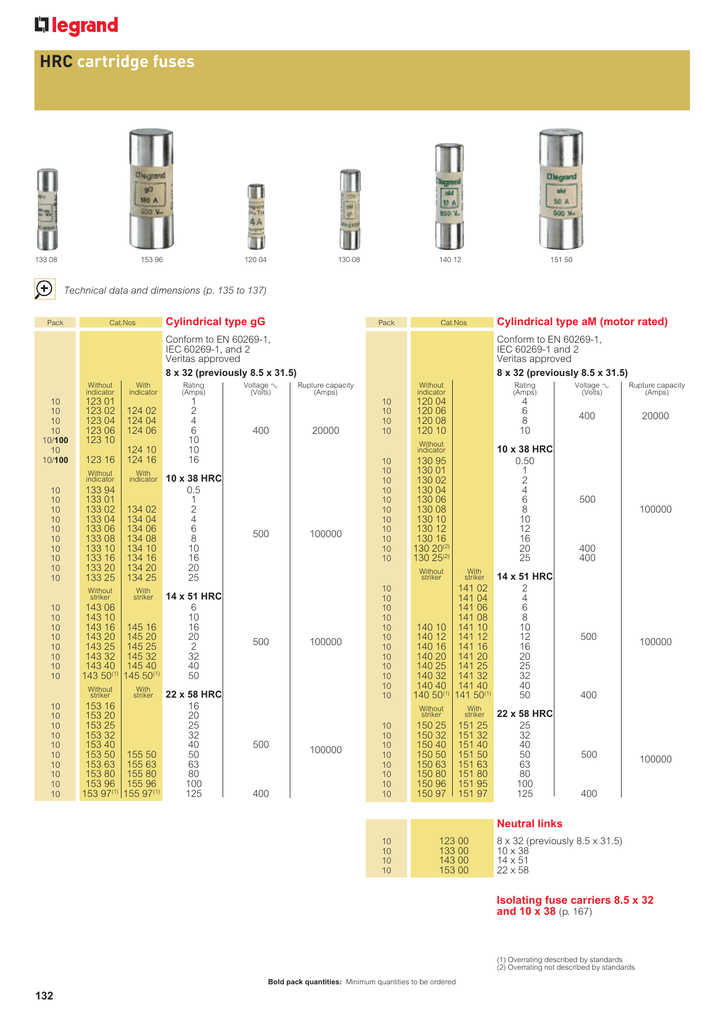
Understanding the HRC Fuse Rating Chart
The HRC fuse rating chart is a crucial reference tool used by engineers and electricians to select the appropriate fuse for a specific application. It contains valuable information about the fuse’s current-carrying capacity, voltage rating, and other technical specifications.
Typically, the HRC fuse rating chart includes:
Rating
- Current Rating (In Amperes): This indicates the maximum current the fuse can carry continuously without tripping.
- Voltage Rating (In Volts): The maximum voltage the fuse can safely handle.
How to Calculate the Fuse Rating
Calculating the fuse rating for your application involves considering factors such as the circuit’s maximum current, ambient temperature, and the type of load. While this process may seem complex, it’s essential to ensure safety and reliability.
To calculate the fuse rating, follow these steps:
- Determine the maximum current: Identify the highest current that the circuit is expected to carry under normal operating conditions.
- Consider ambient temperature: Higher temperatures can affect the fuse’s performance. Check the environmental temperature where the fuse will be installed.
- Account for inrush current: Some equipment may have a momentary surge in current when powered on. Ensure the fuse can handle this inrush without tripping.
- Select the appropriate HRC rating: Refer to the HRC fuse rating chart and choose the HRC rating that matches or exceeds the calculated current.
Selecting the Right HRC Fuse
Choosing the right HRC fuse is a critical decision, as it directly impacts the safety of your electrical system. Factors to consider when selecting an HRC fuse include:
- Circuit Characteristics: Analyze the type of circuit, its load, and the potential fault currents it may encounter.
- Environmental Conditions: Take into account the temperature, humidity, and any corrosive elements present in the installation environment.
- Voltage Requirements: Ensure that the fuse’s voltage rating is suitable for your application.
- Inrush Current: If your equipment experiences inrush current, select a fuse that can handle these brief surges.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation of HRC fuses is crucial for their effectiveness. Ensure that fuses are correctly sized and securely connected to the circuit. Regular maintenance checks are also essential to detect any signs of wear or damage and replace fuses as needed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When dealing with HRC fuses, several common mistakes can compromise safety and performance. Avoid these pitfalls:
- Ignoring the Fuse Rating: Using a fuse with an incorrect rating can lead to overcurrent situations and equipment damage.
- Neglecting Maintenance: Failing to inspect and replace damaged fuses can result in unreliable protection.
- Improper Installation: Incorrectly installing fuses can create loose connections and reduce their effectiveness.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems always carries risks. When dealing with HRC fuses, follow these safety precautions:
- Disconnect Power: Always de-energize the circuit before working on or replacing fuses.
- Use Appropriate PPE: Wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Refer to Manuals: Consult equipment manuals and manufacturer guidelines for specific fuse recommendations.
Applications of HRC Fuses
HRC fuses find applications in various industries and settings, including:
- Industrial Plants: Protecting motors, transformers, and other equipment.
- Residential Electrical Panels: Safeguarding household appliances and circuits.
- Automotive: Preventing electrical faults in vehicles.
- Commercial Buildings: Ensuring safety in electrical distribution systems.
HRC Fuse vs. Other Types of Fuses
While HRC fuses offer many advantages, they are not the only option. It’s essential to understand the differences between HRC fuses and other types, such as ceramic fuses or semiconductor fuses, to make informed decisions.
Benefits of Using HRC Fuses
HRC fuses provide several benefits, including:
- High Rupturing Capacity: They can safely interrupt high fault currents.
- Reliability: HRC fuses are known for their consistent performance.
- Wide Application Range: They are suitable for various industries and environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the HRC fuse rating chart and its significance is essential for electrical safety and circuit protection. By selecting the right fuse rating, following safety precautions, and ensuring proper installation and maintenance, you can safeguard your electrical systems effectively.
FAQs
- What does HRC stand for in HRC fuses?
- HRC stands for High Rupturing Capacity, indicating a fuse’s ability to interrupt high fault currents.
- Can I replace an HRC fuse with a different type of fuse?
- It’s crucial to use the recommended fuse type for your application to ensure safety and reliability.
- What should I do if an HRC fuse keeps blowing?
- Check for underlying electrical issues, such as overloads or short circuits, and consult a professional if necessary.
- Are HRC fuses suitable for outdoor use?
- Some HRC fuses are designed for outdoor applications, but it’s essential to check the manufacturer’s specifications.
- How often should I inspect HRC fuses?
- Regular visual inspections are recommended, and fuses should be replaced if any signs of damage or wear are detected.
Remember that proper knowledge and handling of HRC fuses are crucial for electrical safety, so always seek professional advice when in doubt.
Connect with safety, choose the right HRC fuse for your application, and ensure the uninterrupted flow of electricity.
Maximizing Safety: Understanding Fuse Ratings and Applications
In the realm of electrical safety, understanding fuse ratings is paramount. Fuses act as crucial safeguards against overcurrent situations, preventing electrical circuits from overheating and causing potential hazards. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of fuse ratings, exploring their significance, applications, and the factors that influence their selection.
Unveiling the Fuse Rating Essentials
1. The Significance of Adequate Fuse Ratings
The current rating of a fuse should never fall short of the maximum current it’s expected to handle. To ensure optimal protection, the normal fuse current rating should be at least twice the expected current. This redundancy is vital to ensure that the fuse can perform its primary function – breaking the circuit when the current exceeds safe limits.
2. AC vs. DC Applications
While some AC rated fuses can be used in DC applications, it’s essential to be cautious. When employed in such scenarios, there may be a voltage de-rating, affecting the fuse’s performance. It’s advisable to consult with experts or manufacturers when considering this cross-application.
3. Operating Ambient Temperature
The operating ambient temperature plays a significant role in fuse performance. All Cooper Bussmann British style fuses undergo rigorous testing to meet IEC standards. These standards necessitate a test voltage that is 5% higher than the rated voltage, ensuring reliable operation under various temperature conditions.
Exploring Fuse Selection Factors
4. HRC or “Table C)(15)(a)” Consideration
When selecting fuses, one must consider factors like the HRC or “Table C)(15)(a).” The ambient temperature chart in the FUSE SELECTION CHECKLIST section illustrates how ambient temperature influences the nominal current rating. Making the right choice here is pivotal to ensure the fuse’s effectiveness.
5. High Rupture Capacity (HRC) Fuses
High rupture capacity fuses are capable of interrupting currents up to 1kA. They offer flexibility in applications, allowing fuses of the same category to substitute for each other, provided the circuit’s voltage rating aligns with the fuse rating. When selecting HRC fuses, align them with the operating current to optimize their performance.
6. Understanding the Fuse Rating
The fuse rating is a critical aspect of fuse selection. It should be determined based on the operating current in the circuit. For instance, if a circuit carries a 20A current, a 10A rated fuse would be inadequate. Therefore, it’s imperative to match the fuse rating with the expected current load.
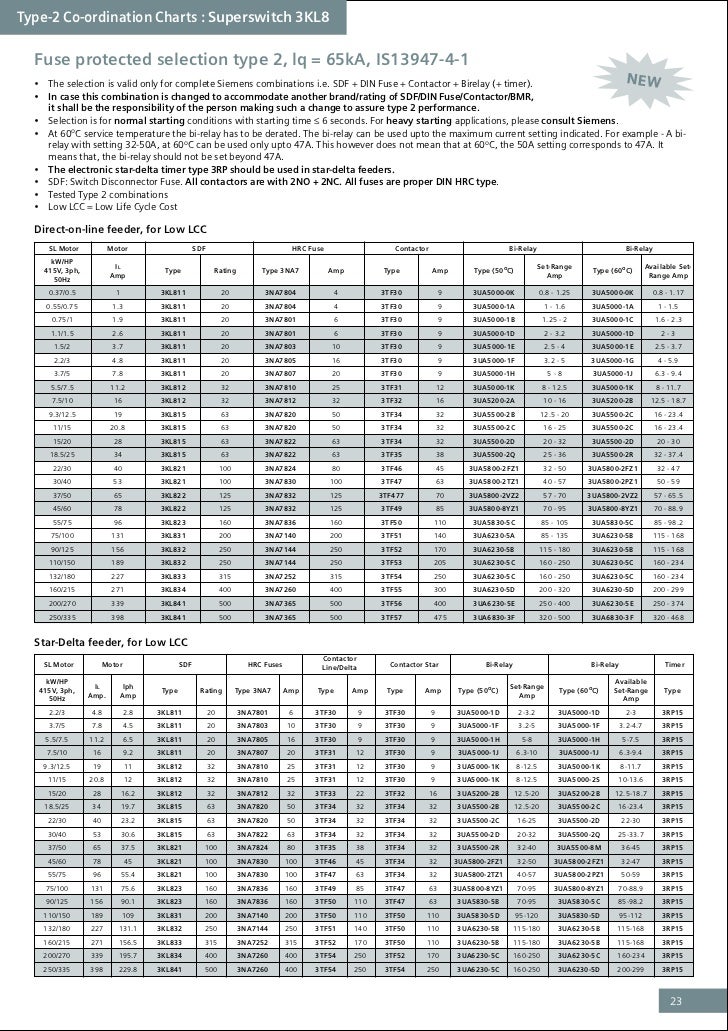
Deciphering the Fuse Chart
7. The Fuse Chart
A helpful tool in the fuse selection process is the fuse chart, illustrating various electrical fuse types. One such type is the high rupturing capacity (HRC) or BS fuse. These charts provide valuable insights into dimensions and applications, aiding in the selection of the appropriate fuse for your specific needs.
8. Current-Limiting Fuses
Current-limiting fuses like H07C, K07C, and L09C offer enhanced protection by limiting the magnitude of current during faults. These fuses help prevent damage to sensitive equipment and mitigate potential electrical hazards. Understanding their let-through characteristics is crucial for optimal utilization.
Calculating Fuse Ratings
9. The Art of Fuse Rating Calculation
Selecting the right fuse often involves calculating the fuse rating accurately. This can be achieved by considering factors like ambient temperature and operating conditions. Accurate calculations ensure that the fuse can perform its protective role effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fuse ratings are not just arbitrary numbers; they are essential components of electrical safety. Choosing the right fuse with the appropriate rating is critical to prevent overheating, electrical fires, and equipment damage. By understanding the factors that influence fuse selection and taking into account the operating environment, you can ensure maximum safety and reliability in your electrical circuits. Remember, when in doubt, consult with experts or refer to manufacturers’ guidelines for the best fuse choice for your specific application.